Immune Response Dynamics
TEL +81-6-6879-4939
FAX +81-6-6879-4938
Overview
Immune regulation by the nervous system
It has long been proposed that various aspects of immune responses are influenced by nervous system activity. Indeed, lymphoid organs are innervated by various types of neurons, and immune cells express neurotransmitter receptors to respond to the neural inputs. However, little is known about how the inputs from the nervous system control immune responses. To solve this problem, we are studying the cellular and molecular basis for the neural regulation of immunity. Adrenergic nerves constitute the efferent arc of the sympathetic nervous system and produce noradrenaline that induces cellular responses through α1-, α2-, β1-, β2- and β3-adrenergic receptors. Like other vital organs, lymphoid organs, including the bone marrow, thymus, spleen and lymph nodes, receive a rich supply of adrenergic nerves. We found that inputs from adrenergic nerves control lymphocyte egress from lymph nodes through β2-adrenergic receptors (J. Exp. Med. 2014, Fig. 1). Additionally, our study demonstrated that this mechanism helps generate a diurnal rhythm of adaptive immune responses in lymph nodes (J. Exp. Med. 2016).
Developing novel therapeutic strategies for inflammatory diseases
Lymphocyte migration is mediated by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that respond to chemoattractants, represented by chemokines. In search of novel factors involved in chemoattractant receptor signaling, we identified a protein complex consisting of copper metabolism MURR1 domain-containing (COMMD) 3 and COMMD8 (COMMD3/8 complex) (J. Exp. Med. 2019). The COMMD3/8 complex interacts with the C-terminal tail of chemoattractant receptors and promotes lymphocyte chemotaxis mediated by the receptors (Fig. 2). Deficiency of the COMMD3/8 complex severely impaired B cell migration in vivo and humoral immune responses. Therefore, the COMMD3/8 complex is essential for proper functioning of the immune system. Our recent data suggest that the COMMD3/8 complex may be involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Pharmacological inhibition of the COMMD3/8 complex may provide a novel approach for the treatment of the immune disorders.
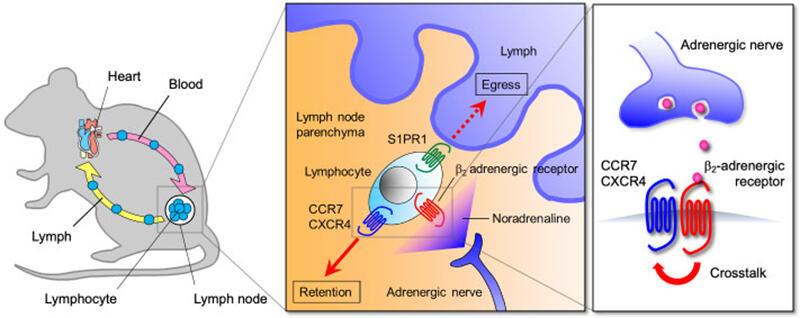
Activation of β2-adrenergic receptors expressed on lymphocytes enhances the responsiveness of CCR7 and CXCR4, chemokine receptors that promote lymph node retention of lymphocytes, and inhibits their egress from lymph nodes.
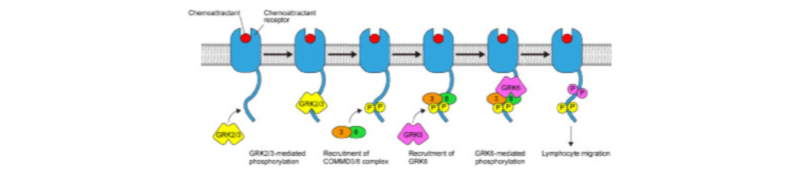
The COMMD3/8 complex functions as an adaptor that recruits GPCR kinase (GRK) 6 to chemoattractant receptors, promoting MAPK activation and consequently lymphocyte chemotaxis.
Principal Investigator
Kazuhiro Suzuki Professor

Research field
Neural regulation of adaptive immunity
Development of novel therapies for inflammatory diseases
Education history
| 2007.9 | PhD, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University |
|---|---|
| 2003.3 | MD, Medical School of Osaka University |
| 1998.3 | BSc, School of Science, The University of Tokyo |
Research and career history
| 2026.1 | Professor (concurrent), IFReC, The University of Osaka |
|---|---|
| 2026.1 | Professor, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Osaka |
| 2017.4 | Professor, IFReC, Osaka University |
| 2011.10 | PRESTO researcher, JST (-2015.3) |
| 2011.4 | Associate professor, IFReC, Osaka University (-2017.3) |
| 2007.10 | Postdoctoral fellow, University of California, San Francisco, USA (-2011.3) |
| 2006.4 | JSPS fellow (DC2) (-2007.9) |
| 2003.4 | Resident in internal medicine, Osaka University Hospital (-2004.3) |
Prize
| 2024 |
JSI Award (Japanese Society for Immunology) |
|---|---|
| 2016 | Medical Research Encouragement Prize (The Japan Medical Association) |
| 2016 | Astellas award for the best biomedical research (The Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders) |
| 2016 | Astellas award for the outstanding presentation (The Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders) |
| 2012 | Young Investigator Award (The Japanese Society of Immunology) |
| 2009 | Inoue Research Award for Young Scientists (The Inoue Foundation for Science) |
| 2008 | Long-term Fellowship (Human Frontier Science Program) |
| 2008 | The Yamamura Prize (Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University) |
| 2003 | The Yamamura Prize (Medical School of Osaka University) |
Members
- Kazuhiro Suzuki Professor
ksuzukiifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp - Taiichiro Shirai Assistant Professor
shiraiifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp - Satomi Komori Assistant Professor
skomoriifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp - Akiko Nakai Visiting Researcher
Achievements
Publications
- Shirai, T., Nakai, A., Ando, E, Fujimoto, J., Leach, S., Arimori, T., Higo, D., van Eerden, F.J., Tulyeu, J., Liu, Y-C., Okuzaki, D., Murayama, M.A., Miyata, H., Nunomura, K., Lin, B., Tani, A., Kumanogoh, A., Ikawa, M., Wing, J.B., Standley, D.M., Takagi, J., Suzuki, K. Celastrol suppresses humoral immune responses and autoimmunity by targeting the COMMD3/8 complex. Sci. Immunol. 8: eadc9324, 2023.
- Nakai, A., Fujimoto, J., Miyata, H., Stumm, R., Narazaki, M., Schulz, S., Baba, Y., Kumanogoh, A. and Suzuki, K. The COMMD3/8 complex determines GRK6 specificity for chemoattractant receptors. J. Exp. Med. 216: 1630-1647, 2019.
- Suzuki, K., Hayano, Y., Nakai, A., Furuta, F. and Noda, M. Adrenergic control of the adaptive immune response by diurnal lymphocyte recirculation through lymph nodes. J. Exp. Med. 213: 2567-2574, 2016.
- Nakai, A., Hayano, Y., Furuta, F., Noda, M. and Suzuki, K. Control of lymphocyte egress from lymph nodes through β2-adrenergic receptors. J. Exp. Med. 211: 2583-2598, 2014.
- Green, J.A., Suzuki, K., Cho, B., Willison, D., Palmer, D., Allen, C.D.C., Schmidt, T.H., Xu, Y., Proia, R., Coughlin, S.R. and Cyster, J.G. The sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor S1P2 maintains the homeostasis of germinal center B cells and promotes niche confinement. Nat. Immunol. 12: 672-680, 2011.
- Suzuki, K., Grigorova, I., Phan, T.G., Kelly, L.M. and Cyster, J.G. Visualizing B cell capture of cognate antigen from follicular dendritic cells. J. Exp. Med. 206: 1485-1493, 2009
- Suzuki, K., Kumanogoh, A. and Kikutani, H. Semaphorins and their receptors in immune cell interactions. Nat. Immunol. 9: 17-23, 2008.
- Suzuki, K., Okuno, T., Yamamoto, M., Pasterkamp, R.J., Takegahara, N., Takamatsu, H., Kitao, T., Takagi, J., Rennert, P.D., Kolodkin, A.L., Kumanogoh, A. and Kikutani, H. Semaphorin 7A initiates T-cell-mediated inflammatory responses through α1β1 integrin. Nature 446: 680-684, 2007.
