News & Topics
Arid5a exacerbates IFN-γ-mediated septic shock by stabilizing T-bet mRNA (Kishimoto group, in PNAS)
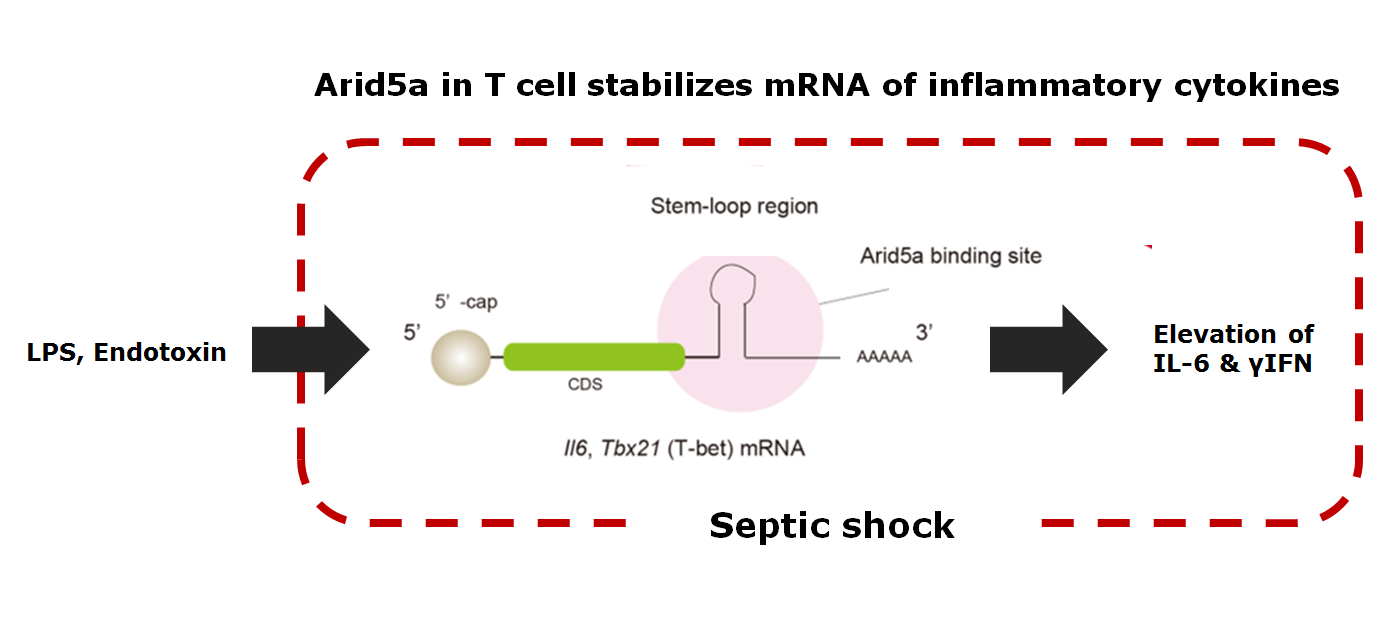
Tadamitsu Kishimoto group (Immune Regulation) revealed that AT-rich interactive domain 5a (Arid5a) accelerates symptoms of septic shock.
Sepsis occurs when pathogen penetrates from the blood stream and spreads thorough out the body, inducing systemic symptoms with secretion of
inflammatory cytokines. Severe sepsis induces septic shock.
The group showed that Arid5a promotes the production of an inflammatory cytokine, IFN-γ, in CD4+ T cells (Th1 cells) by binding to and stabilizing
"T-box expressed in T cells" (T-bet) mRNA, thereby exacerbating symptoms of sepsis. These results suggest that developing a molecule which neutralizes
Arid5a function might link to treatment of septic shock.
Article (External Link)
Contact:
Tadamitsu Kishimoto
Immune Regulation
Immunology Frontier Research Center (WPI-IFReC), Osaka University
