News & Topics
The transcription factor Foxo1 controls germinal center B cell proliferation in response to T cell help (Kurosaki group, in JEM)
Tomohiro Kurosaki's group (Lymphocyte Differentiation) and others have revealed the molecular mechanism of germinal center (GC) B cell proliferation.
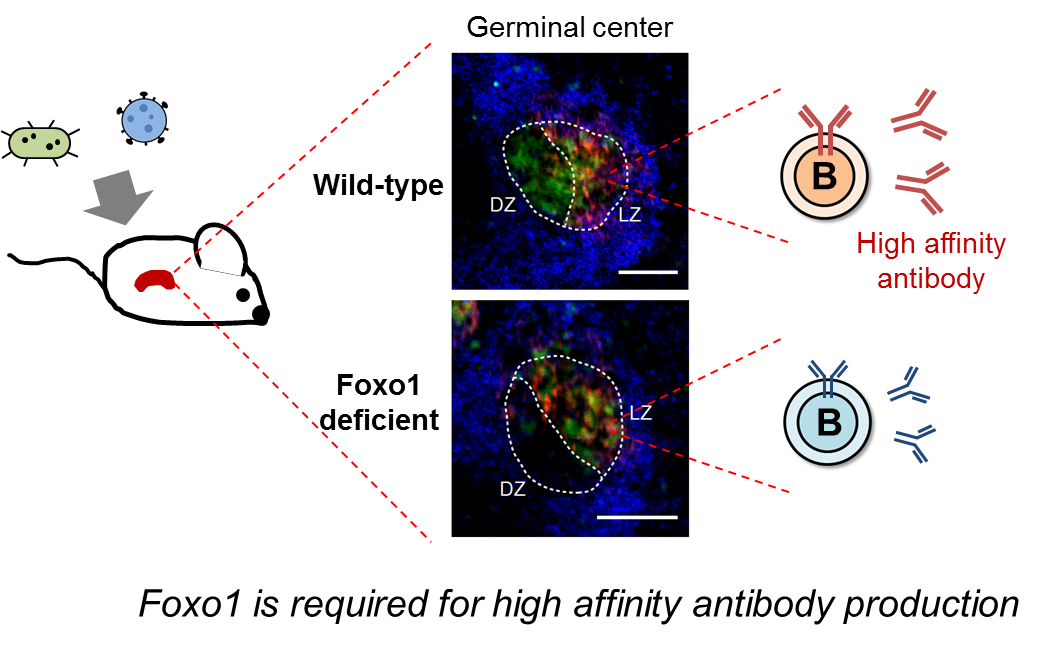
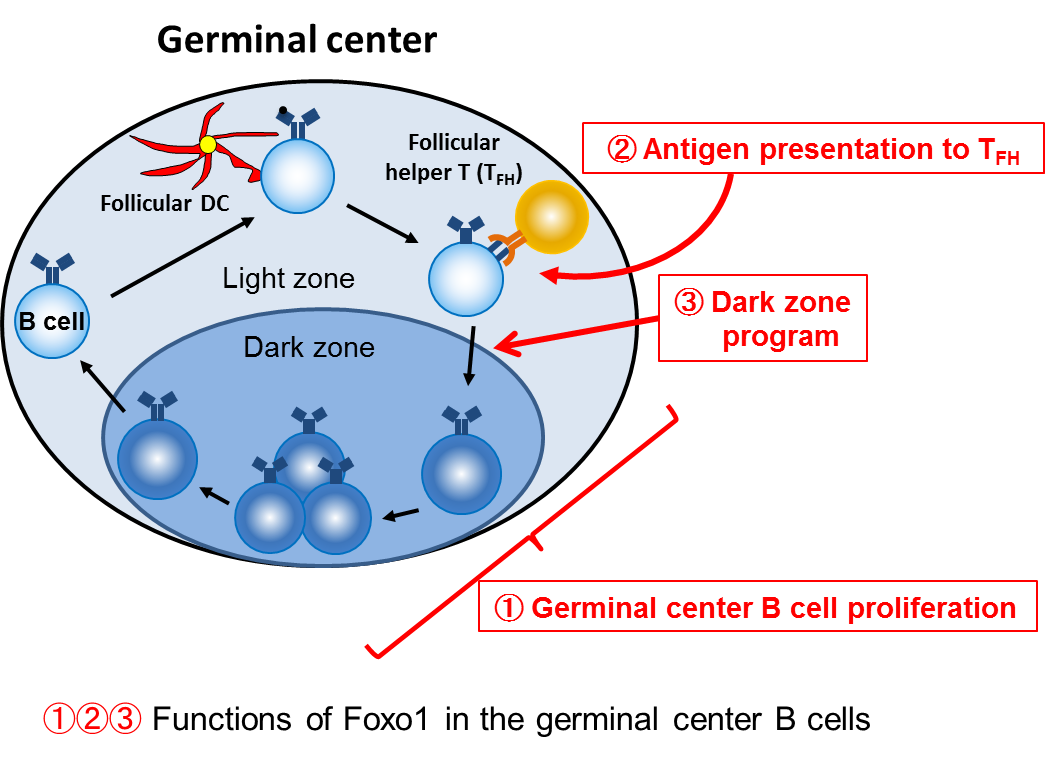
Germinal center (GC) B cells cycle between two states, the light zone (LZ) and the dark zone (DZ). The group demonstrated that ablation of transcription factor Foxo1 after GC development led to the loss of the DZ GC B cells and disruption of the GC architecture. Foxo1-deficient GC B cells also showed less proliferative expansion than controls.
Moreover, the group found that the transcription factor BATF was transiently induced in LZ GC B cells in a Foxo1-dependent manner and that deletion of BATF similarly led to GC disruption.
The results suggest that Foxo1 controls not only GC polarization, but also GC proliferation, at least in part, through mediating BATF expression.
This achievement will help to develop new vaccine strategies by targeting Foxo1 to modulate germinal center B cell biology.
Commentary (PDF)
Article (External Link)
Contact:

Tomohiro Kurosaki(Lymphocyte Differentiation)
![]() +81-6-6879-4456
+81-6-6879-4456 ![]() kurosaki
kurosaki![]() ifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp
ifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp
