免疫・生化学
Biochemistry & Immunology
TEL 06-6879-4951
FAX 06-6879-4950
概要
動物の発生過程では無用の細胞、害となる細胞が形成され除去される。成体においても老化した細胞は速やかに体内から除去される。この除去過程は細胞のアポトーシスと呼ばれる細胞死と、死細胞のマクロファージによる貪食からなりたっているが、その誘導機構、シグナル伝達、生理作用など不明であった。私達はアポトーシスがサイトカイン(Fasリガンド、FasL)で誘導されること、FasLやその受容体Fasの変異がリンパ節や脾臓の肥大化を伴う、自己免疫疾患を発症することを見出した。ついで、この過程にはタンパク質分解酵素カスパーゼが関与していること、カスパーゼによって活性化されるDNA分解酵素により、染色体DNAが分解されることを示した。ついで、私達は、マクロファージによるアポトーシス細胞の貪食法を用いてマクロファージ表面蛋白質に対するモノクローナル抗体を樹立し、貪食に関与する分子を同定した。これらの分子はアポトーシス時に細胞の外側に暴露されるフォスファチジルセリン(PtdSer)を認識した。そして、これら分子を欠損するマウスは歳とともに全身性エリテマトーデス様自己免疫疾患を発症することを見いだした。
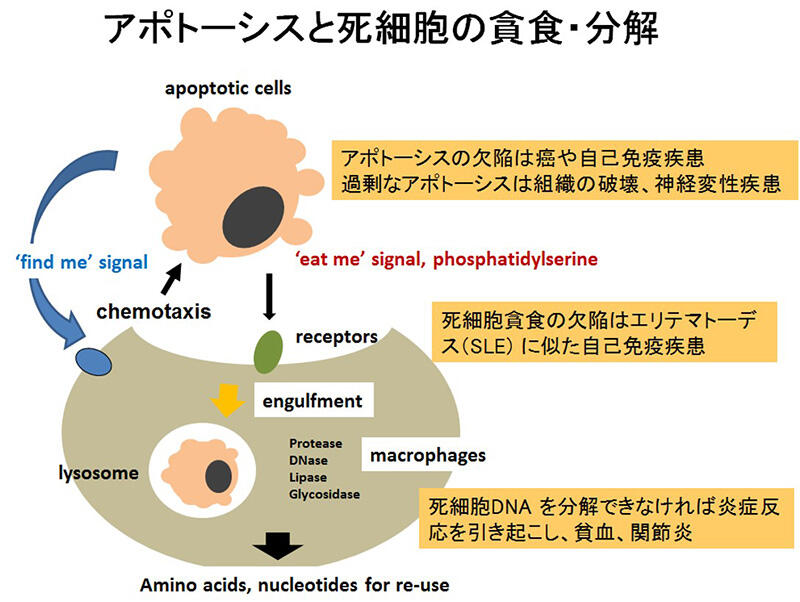
細胞膜を構成するリン脂質は外膜と内膜の間で非対称的に分布されているが、通常、PtdSerはそのすべてが内膜に存在する。私達はPtdSerを外膜から内膜へ移動させるフリッパーゼ、アポトーシス時にPtdSerを内外の膜の間でスクランブルさせるスクランブラーゼを同定した。細胞がアポトーシスに陥ると、フリッパーゼはカスパーゼによって切断、失活し、スクランブラーゼはカスパーゼによって活性化される。また、リン脂質をスクランブルさせる分子にはCa2+によって活性化される分子が存在すること、その分子はScott Syndrome と呼ばれる血友病の原因遺伝子であることも見いだした。現在、これら知見をもとにアポトーシスの分子機構、生理作用を理解するため、以下の課題で研究している。
- アポトーシス細胞の貪食の分子機構
- ノックアウト細胞、ノックアウトマウスを用いたフリッパーゼの生理作用
- ノックアウト細胞、マウスを用いたスクランブラーゼ、その関連分子の生理作用
- フリッパーゼ、スクランブラーゼの作用機構
主任研究者
長田 重一 教授

研究内容
細胞死(アポトーシス)の分子機構とその生理作用
学歴
| 1972 | 東京大学理学部生物化学科卒業 |
|---|---|
| 1977 | 東京大学大学院理学系研究科博士課程修了 |
職歴
| 1977 | 東京大学・医科学研究所・助手 |
|---|---|
| 1977 | チューリッヒ大学・分子生物学研究所・研究員 |
| 1982 | 東京大学・医科学研究所・助手 |
| 1987 | 大阪バイオサイエンス研究所・第一研究部部長 |
| 1995 | 大阪大学・医学部・遺伝学教授 |
| 2002 | 大阪大学大学院・生命機能研究科・教授 |
| 2007 | 京都大学大学院・医学研究科・医化学教授 |
| 2015 | 大阪大学・免疫学フロンティア研究センター・教授 |
受賞・表彰
| 1994.11 | Emil Adolf von Behring Prize (Philipps-Universitat Marburg, Germany) |
|---|---|
| 1995.10 | Robert Koch Award (Koch Foundation, Germany) |
| 1996.11 | ベーリング 北里賞 |
| 1997.1 | Le Prix Antoine Lacassagne (French Cancer League, France) |
| 1998.1 | 朝日賞 |
| 1998.2 | 高松宮妃癌研究基金学術賞 |
| 2000.6 | 恩賜賞・学士院賞 |
| 2001.11 | 文化功労者・顕彰 |
| 2004.6 | International Cell Death Society Prize (Maynooth, Ireland) |
| 2011.1 | 日本学士院・会員 |
| 2012.4 | 名誉博士号 (スイス・チューリッヒ大学) |
| 2012.9 | 日本癌学会 吉田富三賞 |
| 2012.12 | Debrecen Award (Debrecen University, Hungary) |
| 2013.6 | 京都大学孜孜賞 |
| 2013.11 | 慶應医学賞 |
| 2015.4 | アメリカ科学アカデミー(NAS) 外国人会員 |
| 2022.11 | 瑞宝重光章 |
メンバー
- 長田 重一 教授
snagataifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp - 櫻木 崇晴 助教
sakuragiifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp - 瀬川 勝盛 招へい教授
segawa.mchetmd.ac.jp - 鈴木 淳 招へい教授
jsuzukiicems.kyoto-u.ac.jp
業績
論文
- Nagata S, Taira H, Hall A, Johnsrud L, Streuli M, Ecsodi J, Boll W, Cantell K and Weissmann C (1980) Synthesis in E. coli of a polypeptide with human leukocyte interferon activity. Nature 284: 316-320.
- Nagata S, Mantei N and Weissmann C (1980) The structure of one of the eight or more distinct chromosomal genes for human interferon-. Nature 287: 401-408.
- Streuli M, Nagata S and Weissmann C (1980) At least three human type a interferons: structure of 2. Science 209: 1343-1347.
- Taniguchi T, Mantei N, Schwarzstein M, Nagata S, Muramatsu M and Weissmann C (1980) Human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons are structurally related. Nature 285: 547-549.
- Nagata S, Tsuchiya M, Asano S, Kaziro Y, Yamazaki T, Yamamoto O, Hirata Y, Kubota N, Oheda M, Nomura H and Ono M (1986) Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for human granuloctye colony-stimulating factor. Nature 319: 415-418.
- Fukunaga R, Ishizaka-Ikeda E, Seto Y and Nagata S (1990) Expression cloning of a receptor for murine granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Cell 61: 341-350.
- Itoh N, Yonehara S, Ishii A, Yonehara M, Mizushima S, Sameshima M, Hase A, Seto Y and Nagata S (1991) The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 66: 233-243.
- Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA and Nagata S (1992) Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature 356: 314-317.
- Fukunaga R, Ishizaka-Ikeda E and Nagata S (1993) Growth and differentiation signals mediated by two distinct regions in the cytoplasmic domain of G-CSF receptor. Cell 74: 1079-1087.
- Ogasawara J, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Adachi M, Matsuzawa A, Kasugai T, Kitamura Y, Itoh N, Suda T and Nagata S (1993) Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature 364: 806-809.
- Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P and Nagata S (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand: a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell 75: 1169-1178.
- Kägi D, Vignaux F, Ledermann B, Burki K, Depraetere V, Nagata S, Hengartner H and Golstein P (1994) Fas and perforin pathway as major mechanisms of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Science 265: 528-530.
- Takahashi T, Tanaka M, Brannan CI, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Suda T and Nagata S (1994) Generalized lymphoproliferative disease in mice, caused by a point mutation in the Fas ligand. Cell 76: 969-976.
- Enari M, Hug H and Nagata S (1995) Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature 375: 78-81.
- Enari M, Talanian RV, Wong WW and Nagata S (1996) Sequential activation of ICE-like and CPP32-like proteases during Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature 380: 723-726.
- Tanaka M, Suda T, Haze K, Nakamura N, Sato K, Kimura F, Motoyoshi K, Mizuki M, Tagawa S, Ohga S, Hatake K, Drummond A and Nagata S (1996) Fas ligand in human serum. Nat. Med. 2: 317-322.
- Kondo T, Suda T, Fukuyama H, Adachi M and Nagata S (1997) Essential roles of the Fas ligand in the development of hepatitis. Nat. Med. 3: 409-413.
- Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A and Nagata S (1998) A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature 391: 43-50.
- Sakahira H, Enari M and Nagata S (1998) Cleavage of CAD inhibitor in CAD activation and DNA degradation during apoptosis. Nature 391: 96-99.
- Tanaka M, Itai T, Adachi M and Nagata S (1998) Down-regulation of Fas ligand by shedding. Nat. Med. 4: 31-36.
- Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Kondoh G, Takeda J, Ohsawa Y, Uchiyama Y and Nagata S (2001) Requirement of DNase II for definitive erythropoiesis in the mouse fetal liver. Science 292: 1546-1549.
- Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miwa K, Shinohara A, Iwamatsu A and Nagata S (2002) Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 417: 182-187.
- Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Yoshida H, Nagase H, Ohsawa Y, Uchiyama Y, Iida T, Okada K and Nagata S (2003) Impaired thymic development in mouse embryos deficient in apoptotic DNA degradation. Nat. Immunol 4: 138-144.
- Nishimoto S, Kawane K, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukuyama H, Ohsawa Y, Uchiyama Y, Hashida N, Ohguro N, Tano Y, Morimoto T, Fukuda Y, and Nagata S (2003). Nuclear cataract caused by a lack of DNA degradation in the mouse eye lens. Nature 424: 1071-1074.
- Hanayama R, Tanaka M, Miyasaka K, Aozasa K, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, and Nagata S (2004). Autoimmune disease and impaired uptake of apoptotic cells in MFG-E8-deficient mice. Science 304: 1147-1150.
Yoshida H, Okabe Y, Kawane K, Fukuyama H, and Nagata S (2005). Lethal anemia caused by interferon- produced in mouse embryos carrying undigested DNA. Nat. Immunol 6: 49-56 - Yoshida H, Kawane K, Koike M, Mori Y, Uchiyama Y, and Nagata S (2005). Phosphatidylserine- dependent engulfment by macrophages of nuclei from erythroid precursor cells. Nature 437: 754-758.
- Kawane K, Ohtani M, Miwa K, Kizawa T, Kanbara Y, Yoshioka Y, Yoshikawa H and Nagata S (2006) Chronic polyarthritis caused by mammalian DNA that escapes from degradation in macrophages. Nature 443: 998-1002.
- Miyanishi, M., Tada, K., Koike, M., Uchiyama, Y., Kitamura, T., and Nagata, S. (2007) Identification of Tim-4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 450: 435-439.
- Okabe, Y., Sano, T. and Nagata, S. (2009) Regulation of the innate immune response by threonine phosphatase of Eyes absent. Nature 460: 520-524
- Suzuki, J., Umeda, M., Sims JP. and Nagata, S. (2010) Calcium-dependent phospholipid scrambling by TMEM16F. Nature 468: 834-838.
- Suzuki, J., Denning, DP., Imanishi, E., Horvitz, HR. and Nagata, S. (2013) Xk-related protein 8 and CED-8 promote phosphatidylserine exposure in apoptotic cells. Science 341: 403-406.
- Segawa, K., Kurata, S., Yanagihashi, Y., Brummelkamp, T., Matsuda, F., and Nagata, S. (2014) Caspase-mediated cleavage of phospholipid flippase for apoptotic phosphatidylserine exposure. Science 344, 1164-1168
主な総説
Nagata S and Golstein P (1995) The Fas death factor. Science 267: 1449-1456.
Nagata S (1997) Apoptosis by death factor. (Review) Cell 88: 355-365.
Nagata S (1999). Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. Annu Rev Genetics 33: 29-55.
Nagata S (2005). DNA degradation in development and programmed cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 853-875.
Nagata, S., Hanayama, R. and Kawane, K. (2010) Autoimmunity and the Clearance of Dead Cells. Cell 140: 619-630.
