免疫機能統御学
Immune Regulation
TEL 06-6879-4957
FAX 06-6879-4958
概要
Introduction to our Laboratory.
The discovery of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and elucidation of its associated receptor signaling pathway, highlighted the important role of cytokines in regulating immune cells. When cytokines become aberrantly regulated, this leads to the inappropriate activation of immune cells. In some cases, this is an important step in the development of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (activation of IL-6 signaling) and systemic lupus erythematosus (activation of type-I interferon signaling). The current challenges, and principal aims of our research, are to make advances in our understanding of the mechanisms of autoimmune disease and related cytokine signaling pathways, to ultimately improve health care- thus "from bench to bedside".
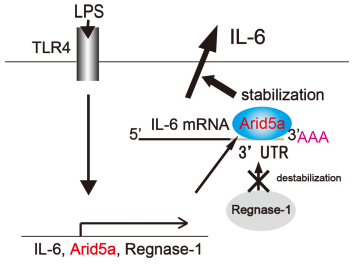
A Summary of our Recent Research. Arid5a controls IL-6 mRNA stability, which contributes to elevation of IL-6 level in vivo
Post-transcriptional regulation of IL-6 has been largely uncharacterized, with the exception of the RNase Regnase-1, which prevents autoimmunity by destabilizing IL-6 mRNA. Here, we identified a novel RNA binding protein, AT-rich interactive domain 5a (Arid5a), which stabilizes IL-6 but not TNF-α mRNA through binding to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of IL-6 mRNA. Arid5a was enhanced in macrophages in response to LPS, IL-1β and IL-6. Arid5a deficiency inhibited elevation of IL-6 serum level in LPS-treated mice, and suppressed IL-6 levels and the development of TH17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Importantly, Arid5a inhibited the destabilizing effect of Regnase-1 on IL-6 mRNA. These results indicate that Arid5a plays an important role in promotion of inflammatory processes and autoimmune diseases.
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of miR-132/212 cluster enhances TH17 cell differentiation
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) has critical roles in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) by controlling Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-producing T helper cells (TH17 cells) and Regulatory T cells (Treg cells). Although various transcription factors and cytokines have been identified as key participants in TH17 generation, the role of microRNA is poorly understood. We found that miR-132/212 cluster is induced by AHR activation under TH17 -inducing, but not Treg cell-inducing conditions. miR-132/212 cluster deficiency abrogated enhancement of TH17 cell differentiation by AHR activation. We identified Bcl-6, a negative regulator of TH17 cell differentiation, as a potential target of miR-132/212 cluster. We investigated the roles of miR-132/212 cluster in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a murine model of MS. miR-132/212 cluster deficient mice showed resistance to the development of EAE and decreased frequency of both TH1 and TH17 cells in draining lymph nodes. Our findings indicate the novel mechanism of AHR-dependent TH17 cell differentiation via miR-132/212 cluster.
Type-I interferon controls its own production in immune homeostasis by inducing PPAR-γ expression and an inhibitory PPAR-γ/IRF7 complex
Type-I interferon is important for anti-viral immunity, but its over-production is linked to the development of autoimmunity. Type-I interferon production requires the transcription factor IRF7. How type-I interferon signals to attenuate its own production in immune homeostasis is not known. Here we show that type-I interferon induces expression of PPAR-γ, which forms an inhibitory interaction with IRF7, attenuating type-I interferon production via the virus-activated (MyD88-independent) pathways in fibroblasts and TLR-activated (MyD88-dependent) pathways in pDCs, and type-I IFN-dependent responses in autoimmunity. Thus all aspects of the type-I IFN system, its production in innate and adaptive immunity and associated immunopathology, are self-controlled through a two-step process of (i) type-I IFN-induced PPAR-γ expression and (ii) formation of an inhibitory PPAR-γ/IRF7 complex.
Therapeutic targeting of the interleukin-6 receptor.
Our research is engaged in clinical studies on the effectiveness of anti-IL6R antibody (Tocilizumab) in autoimmune diseases.
Tocilizumab can inhibit bone resorption and joint destruction in chronic rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients by a large-scale randomized control trial. This effect is due to the inhibitory effect of IL-6 signal blockade on the expression of Rank-ligand and differentiation into osteoclasts of mononuclear cells.
A randomized placebo-controlled phase III trial confirmed that Tocilizumab is effective and safe in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). The USA and EU approved the use of Tocilizumab for the treatment of JIA. In December 2012, large-scale clinical trials for JIA in Europe and the USA confirmed efficacy and safety of Tocilizumab.
Other autoimmune inflammatory diseases have been treated with Tocilizumab, including refractory relapsing polychondritis, AA amyloidosis, reactive arthritis, polymyalgia rheumatica, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis and acquired hemophilia A. The results confirmed efficacy and safety of Tocilizumab in these diseases.
主任研究者
岸本 忠三 特任教授

研究内容
IL-6によるTreg/Th17細胞分化の制御機構の解明および抗IL-6受容体抗体をツールとした免疫難病発症機構の解明
学歴
| 1969.3 | 大阪大学大学院医学研究科 博士修了 |
|---|
職歴
| 1974.11 | 大阪大学医学部助手 |
|---|---|
| 1979.4 | 大阪大学医学部教授 |
| 1983.7 | 大阪大学細胞工学センター教授 |
| 1995.8 | 大阪大学医学部長 |
| 1997.8 | 大阪大学総長 |
| 2003.9 | 大阪大学生命機能研究科教授 |
| 2011.9〜 | 大阪大学免疫学フロンティア研究センター特任教授 |
受賞・表彰
| 1988 | 朝日賞 |
|---|---|
| 1991.4 | 米国国立科学アカデミー外国人会員 |
| 1992.6 | 恩賜賞・日本学士院賞 |
| 1995.12 | 日本学士院会員 |
| 1998.11 | 文化勲章 |
| 2003.10 | ロベルト・コッホゴールドメダル |
| 2009.5 | クラフォード賞 |
| 2011.1 | 日本国際賞 |
| 2017.1 | キング・ファイサル国際賞 |
| 2019.9 | 慶應医学賞 |
| 2020.6 | Tang Prize(唐奨) |
| 2021.9 | クラリベイト引用栄誉賞 |
Kang Sujin 准教授

学歴
| 2005.09 | 大阪大学工学研究科 修士課程修了 |
|---|---|
| 2012.03 | 大阪大学医学系研究科 博士課程 修了 |
職歴
| 2011-2012 | 日本学術振興会 特任研究員DC2 |
|---|---|
| 2012-2014 | 大阪大学未来戦略機構 特任助教 |
| 2014-2017 | 同学医学系研究科・抗体臨床応用学・助教 |
| 2017-2021 | 同学免疫学フロンティア研究センター・免疫機能統御学 寄付研究部門助教 |
| 2021-現在 | 同学免疫学フロンティア研究センター・免疫機能統御学 寄付研究部門准教授 |
受賞・表彰
| 2020 | 令和2年度大阪大学賞 |
|---|---|
| 2020 | 令和2年度文部科学大臣表彰 若手科学者賞 |
| 2018 | 第18回 日本免疫学会研究奨励賞 |
メンバー
-
岸本 忠三 教授
kishimotoifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp -
Kang Sujin 准教授
kangifrec.osaka-u.ac.jp
主な論文(岸本 忠三)
- IL-6 and its receptor ; A paradigm for cytokines. Science 258: 593-597 1992.
- Cytokine signal transduction. Cell 76: 253-262 1994.
- Structure and function of a new STAT-induced STAT inhibitor-1. Nature 387: 924-929 1997.
- Interleukin 6: from bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2(11): 619-626 2006.
- IL-6-dependent and -independent pathways in the development of interleukin 17-producing T helper cells. Proc. Natl. Acsd. Sci. USA. 104: 12099-12104 2007.
- Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, withdrawal phase III trial. Lancet. 371(9617): 998-1006 2008.
主な論文 (Kang Sujin)
- Kishimoto T* and Kang S*. IL-6 Revisited: From Rheumatoid Arthritis to CAR T cell Therapy and COVID-19. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 40:323-48, 2022 (*Equally contributed)
- Kang S*, Kishimoto T*. Interplay between interleukin-6 signaling and the vascular endothelium in cytokine storms. Exp Mol Med. 12:1-8. 2021 (*Corresponding author)
- Kang S, Tanaka T, Inoue H, Ono C, Hashimoto S, Kioi Y, Matsumoto H, Matsuura H, Matsubara T, Shimizu K, Ogura H, Matsuura Y, Kishimoto T. IL-6 trans-signaling induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 from vascular endothelial cells in cytokine release syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A., 117(36): 22351-22356, 2020
- Kang S, Narazaki M, Hozaifa M, Kishimoto T. Historical overview of the interleukin-6 family cytokine. J Exp Med. 217(5); e20190347, 2020
- Kang S*, Kumanogoh A*, The spectrum of macrophage activation by immunometabolism. Int Immunol. 16:dxaa017, 2020, (*Corresponding author)
- Kang S, Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity, 50(4):1007-1023, 2019
- Kang S*, Nakanishi Y, Kioi Y, Okuzaki D, Kimura T, Takamatsu H, Koyama S, Nojima S, Nishide M, Hayama Y, Kinehara Y, Kato Y, Nakatani T, Shimogori T, Takagi J, Toyofuku T, Kumanogoh A*. Semaphorin 6D reverse signaling controls macrophage lipid metabolism and anti-inflammatory polarization. Nat Immunol. 19 (6), 561-570, 2018 (*Corresponding author)
- Kang S, Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. Therapeutic uses of anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody. Int Immunol. 27(1):21-9. 2015
- Kang S, Kumanogoh A. Semaphorins in bone development, homeostasis, and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 24(3):163-71. 2013
- Kang S, Okuno T, Takegahara N, Takamatsu H, Nojima S, Kimura T, Yoshida Y, Ito D, hmae S, You DJ, Toyofuku T, Jang MH, Kumanogoh A. Intestinal epithelial cell-derived semaphorin 7A negatively regulates development of colitis via αvβ1 integrin. J Immunol. 1;188(3):1108-16. 2012
