News & Topics
MACROH2A1 was identified as a biomarker associated with refractory COVID‑19 (Takeda and Kumanogoh G, in Inflamm Regen.)
The COVID-19 pandemic is widespread; however, accurate predictors of refractory cases have not yet been established.
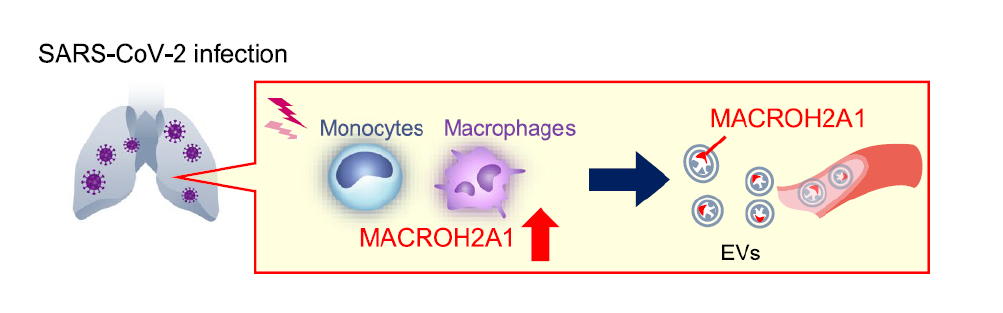
Takahiro Kawasaki (Immunopathology, IFReC), Yoshito Takeda (Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University), and the research group discovered that MACROH2A1 in extracellular vesicles is a potential biomarker of refractory COVID-19 and may reflect the pathogenesis of COVID-19 in monocytes.
 Figure
Figure
In response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, immune response including TLR signaling and cytokine secretion such as INF-gamma enhances expression of MACROH2A1 in monocytes. Subsequently, MACROH2A1 is secreted in circulating exosomes, which are more abundant in severely ill patients with COVID-19 than in those who are not.
Commentary (PDF)
Article (External Link)
Contact:

Atsushi Kumanogoh(Immunopathology)
Immunology Frontier Research Center, Osaka University (WPI-IFReC)
